Starting to exercise is one of the best choices you can make for your health. The best exercise program isn't one-size-fits-all—it's tailored to your goals, fitness level, and lifestyle. This guide will guide you through creating a program that works for you.
What determines the best exercise program?
A great exercise program is:
- goal: Tailored to your specific needs - whether it's weight loss, strength building, improved endurance, or overall health.
- balance: Includes a mix of cardio, strength training, flexibility, and recovery.
- Can be adjusted: Adjust to your fitness level and lifestyle.
- sustainable: Encourage consistency over perfection for long-term results.
Step 1: Set clear goals
Determine what you want to achieve.
Writing down your goals and tracking your progress can increase motivation.
Step 2: Elements of an effective project
A well-rounded exercise program incorporates various components that work together to optimize your physical and mental health. Each element has a unique role in creating balance and sustaining regularity. To comply with recommended health standards, consider Physical activity guidelines:
- participate 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- included Exercise to strengthen muscles For all major muscle groups at least 2-3 times a week.
Here's how these tips translate into actionable steps:
1. Cardiovascular exercise
Cardiovascular exercise Essential for heart health, improving endurance, and burning calories. It enhances your body's ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles, improving overall endurance.
Important benefits:
- Improve cardiovascular health.
- Helps in weight management by burning calories.
- Improve mood by releasing endorphins.
How to combine Cardio:
- Beginners: Start with low-impact activities such as walking, swimming or cycling for 20–30 minutes, 3–4 times a week.
- Intermediate/Advanced level: composed High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) 2-3 times a week. HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by rest (eg sprint for 30 seconds, rest 1 minute, repeat for 15 minutes).
Example activities:
- Brisk walking: 3 kilometers per hour for 30 minutes.
- Jogging: Run 1 mile followed by a light jog.
- Swimming: 20 laps with slow and fast intervals.
2. Strength training
Strength training builds muscle, increases metabolism, and improves density. of bones. It's not just about lifting heavy weights; Even bodyweight exercises can be highly effective.
Important benefits:
- Increase muscle mass, which helps burn more calories at rest.
- Improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury.
- Improve posture and functional strength for daily activities.
How to combine strength training:
- Beginners: to begin with Exercise weight Such as squats, push-ups, and planks. Aim for 2-3 rounds per week, with 8-12 reps per exercise.
- Intermediate/Advanced level: Gradually increase the weight (dumbbells, kettlebells, or barbells) and incorporate compound movements such as deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups. In addition, Full body strength program 3×5 A simple but effective way to build a solid foundation. Include the strength training you want in your exercise program based on your personal preferences.
A typical example for functional exercise:
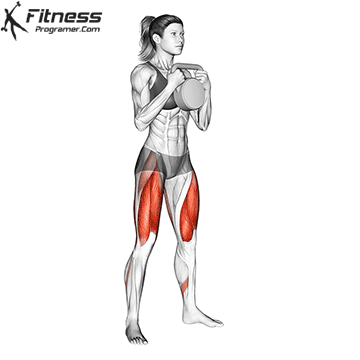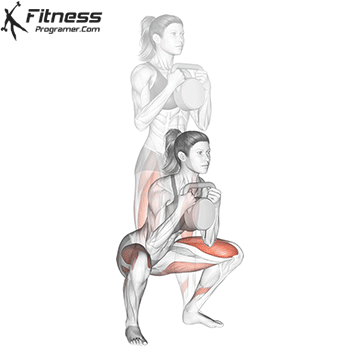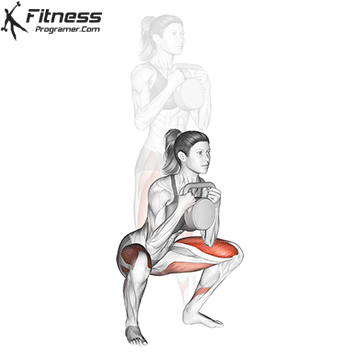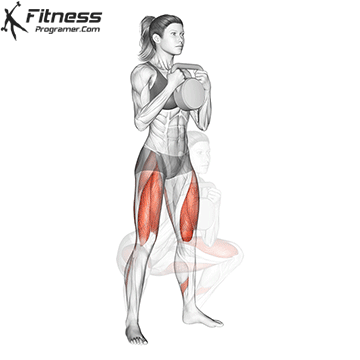
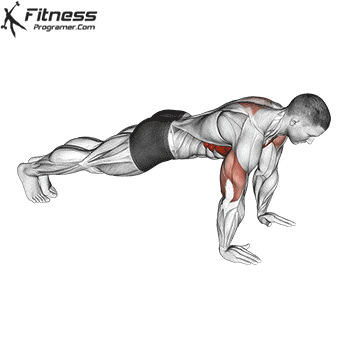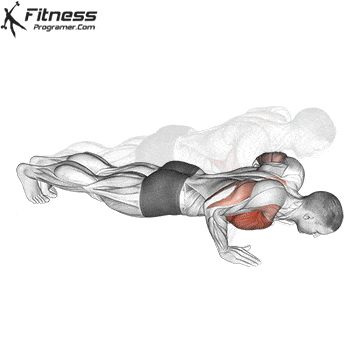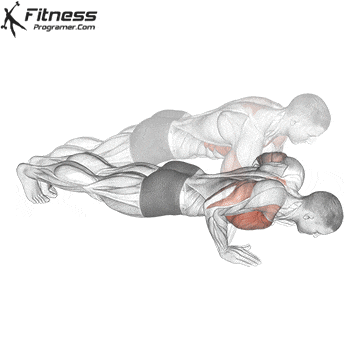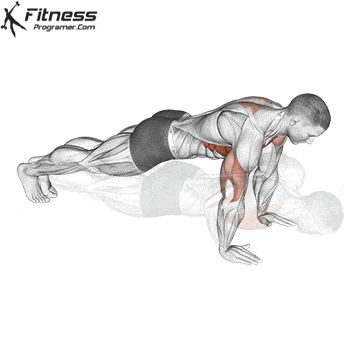
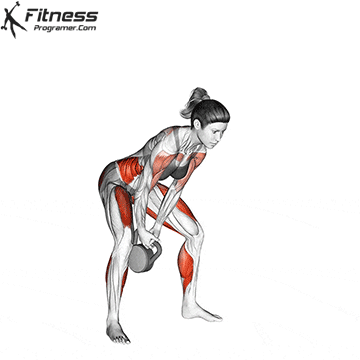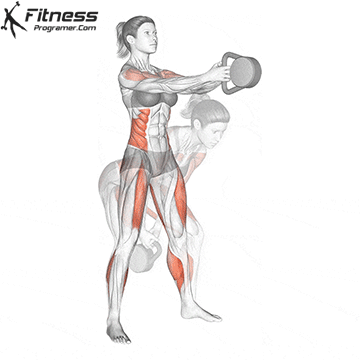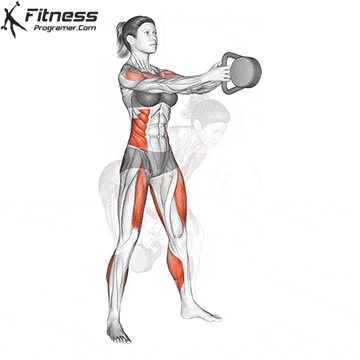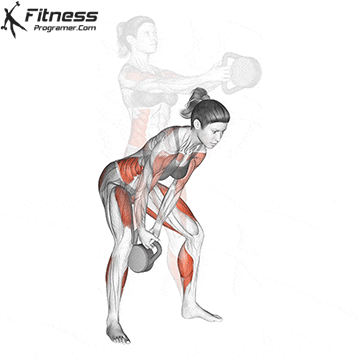
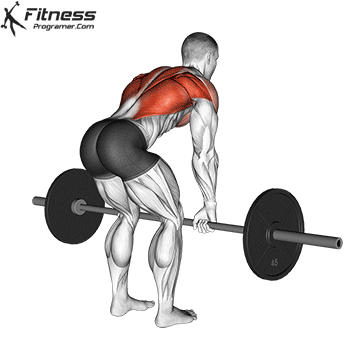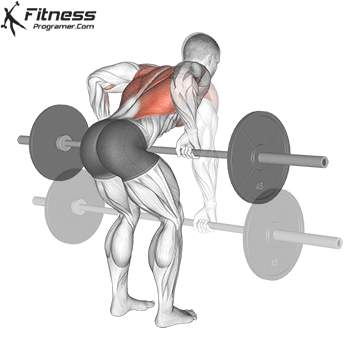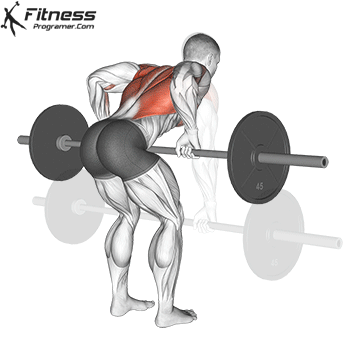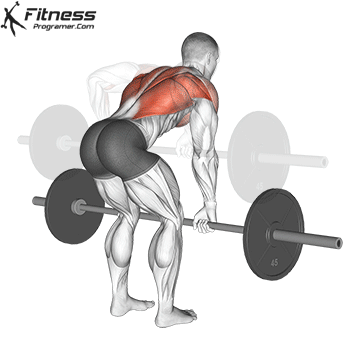
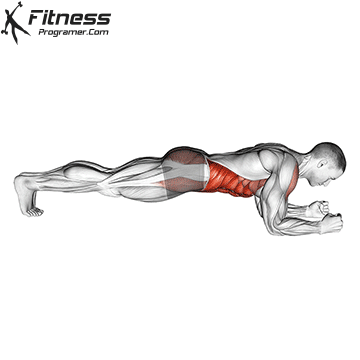
Progress tips: Increase resistance or repetitions every 2–3 weeks to challenge your muscles.
3. Flexibility and mobility
Flexibility and mobility exercises enhance your mobility, reduce muscle stiffness, and prevent injury. These exercises are often overlooked but are important for overall fitness.
Important benefits:
- Improve joint health and function.
- Reduce the risk of injury during exercise.
- Improve recovery and reduce muscle tension.
How to incorporate flexibility training:
- Dynamic stretching: Perform these exercises before exercise Warm up Muscles and improve the level of movement (such as leg swings, arm circles).
- Static stretches: hold stretches for 20-30 seconds after exercise Cool down and improve flexibility (for example, hamstring stretch, chest stretch).
- Yoga or Pilates: Include 20-30 minutes once or twice a week for body flexibility.
A typical example:
- Cat-Cow stretch: 10 reps to mobilize the spine.
- 90/90 stretch: 20 reps to activate the inner leg.
- Hip flexor stretch: Hold for 20 seconds on each side.
- Downward Dog Pose: Hold for 20-30 seconds.

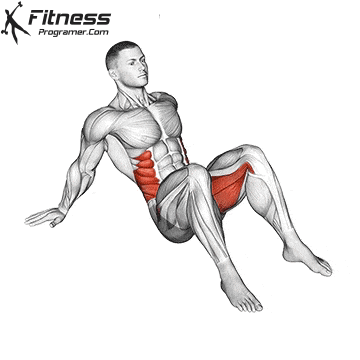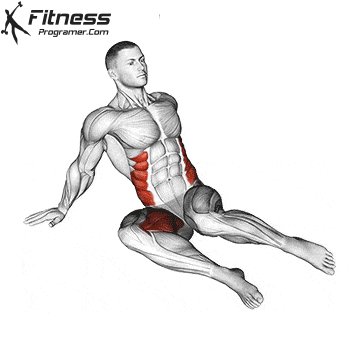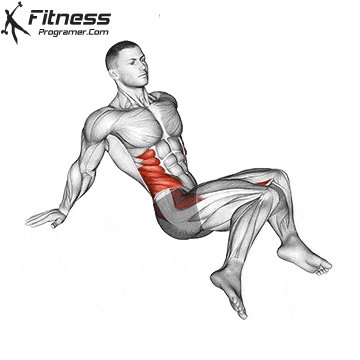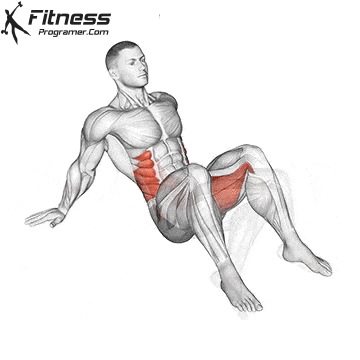
4. Recovery
Recovery is when your body repairs muscles, replenishes energy, and adapts to the stress of exercise. Without adequate recovery, you are at risk of overtraining and injury.
Important benefits:
- Promote muscle growth and recovery.
- Prevent burnout and mental fatigue.
- Improve performance during future workouts.
How to optimize recovery:
- Day off: Full rest 1-2 days a week. Engage in active recovery activities such as light walking or stretching.
- sleep: Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night, as it is important for muscle repair.
- Humidity: Drink enough water to help restore muscles and reduce pain.
- Nutrition: Eat protein-rich foods after exercise to repair muscle tissue. Include carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores.
Sample recovery techniques:
- Foam roller: Focus on tight muscles for 5-10 minutes.
- Ice bath or reverse shower: Immerse yourself in hot and cold water alternately to improve circulation.
- Meditation or breathing: Reduces stress and promotes mental recovery.
Step 3: Sample exercise program
Beginner Exercise Program (Weeks 1–4)
goal: Create a foundation of fitness.
- Day 1: Cardio – 20-30 minute brisk walk or bike ride.
- Day 2: Strength - 3 sets of 10-12 reps for goblet squats, kettlebell swing, bent over rows, push-ups (correct if necessary), and planks (20-30 second hold).
- Day 3: Flexibility – 15 minutes of yoga or stretching.
- Day 4: Cardio – 30 minute walk or swim.
- Day 5: Strength – Do the 2nd day exercise or try Resistance band.
- Day 6: Active recovery – light yoga or nature walks.
- Day 7: Rest.
Moderate Exercise Program (Weeks 5–8)
goal: Improve endurance and strength.
- Day 1: HIIT – 20 seconds work / 10 seconds rest for burpees, jump squats, mountain climbers (15 minutes).
- Day 2: Strength – A typical example for functional alignment Or 3×5 full body strength program
- Day 3: Flexibility – 20 minutes of yoga focusing on hamstrings and shoulders.
- Day 4: Cardio – 30 minutes of running or cycling.
- Day 5: Strength – repeat day 2 workout
- Day 6: Active Recovery – Foam roller or mobile work.
- Day 7: Rest.
Advanced Fitness Program (Week 9 and beyond)
goal: Increase strength, endurance, and maximum flexibility.
- Day 1: Strength – A typical example for functional alignment or 3×5 full body strength program
- Day 2: Cardio – 40 minute run or HIIT with kettlebells.
- Day 3: Flexibility – Deep yoga flow or advanced movement practice.
- Day 4: Strength – repeat day 1 workout
- Day 5: Cardio – Endurance-based: swim or bike for 45 minutes.
- Day 6: Recovery – contrast bath or massage therapy.
- Day 7: Rest.
Step 4: Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Lack of time:
- Choose short high-intensity workouts like HIIT.
- Break up exercise into 10-minute chunks throughout the day.
- Plateau:
- Mix up your activity by trying new exercises.
- Gradually increase the weight, repetitions, or intensity.
- Motivation Dips:
- Set small, achievable goals and celebrate progress.
- Exercise with a friend or join an exercise class for accountability.
Nutrition and lifestyle advice
To enhance your exercise program:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on lean protein, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and lots of vegetables.
- Maintain moisture: Drink water before, during, and after exercise.
- Prioritize sleep: Quality sleep is important for recovery and performance.
Summary
The best exercise program is one that keeps you motivated and aligned with your goals. By addressing each of these components, you create a program that supports your overall fitness, reduces your risk of injury, and sets you up for long-term success. Remember, exercise is a journey, not a destination. Start today and enjoy your journey to stronger, healthier health!
Source link
