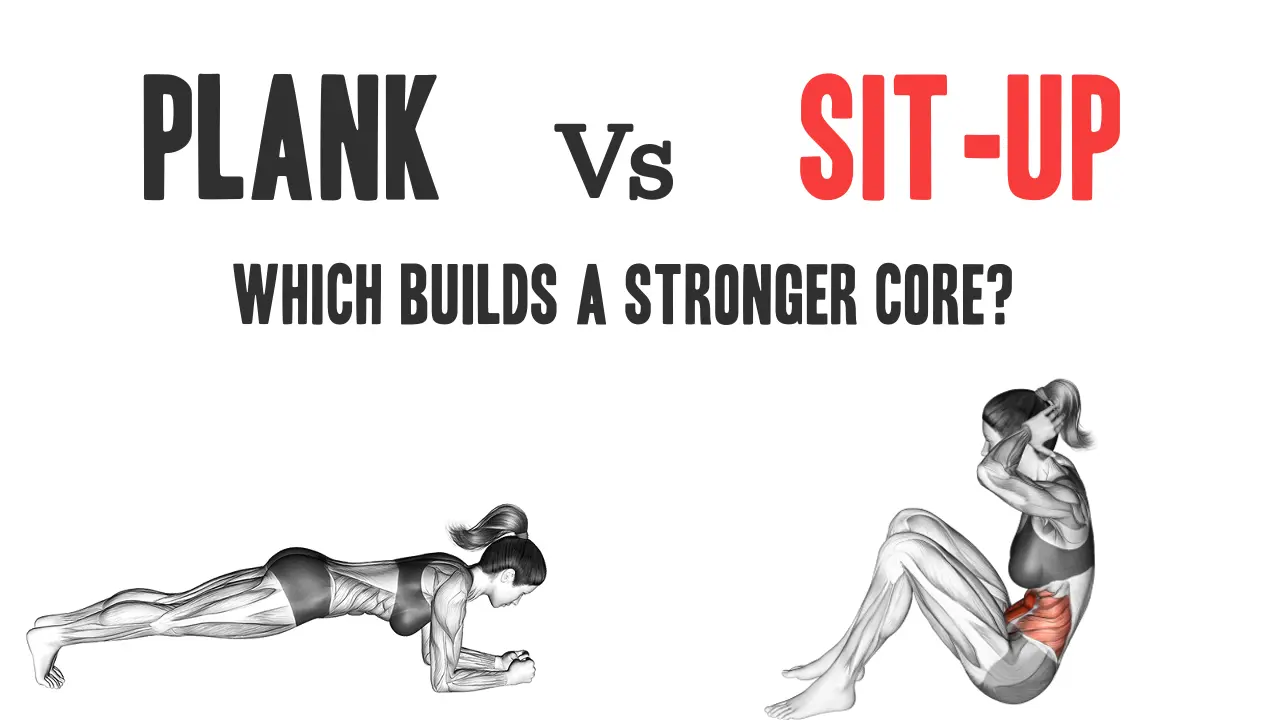
In a strong pursuit, very helpful CoffinA very popular lifter and personality and enthusiasm often woven: should I put more in the boards or seats sitting? While both exercises are well known, they take different ways to the main train.
Have Panel Yes Isometric exercises That shows stability, control of the should, should be muscular patience.
On the other hand, the Sit up Is a Dynamic movement That works at the abdomen through the spine, emphasizing the mobility and strength in contraction.
Each of your own ways - and restrictions - depends on your training goal, your health, and overall movement quality. This article will check Difference between Planks and SIT-UPSEdit the subjects such as: Main activation, Health in the world, Key StrengthAnd Useful performanceHelp you decide what is best that is right for your work.
Core Anatomy: What strength is we trying to strengthen?
Period "Keys" Include more than just a visual fluid muscle. Important ingredients of the core include:
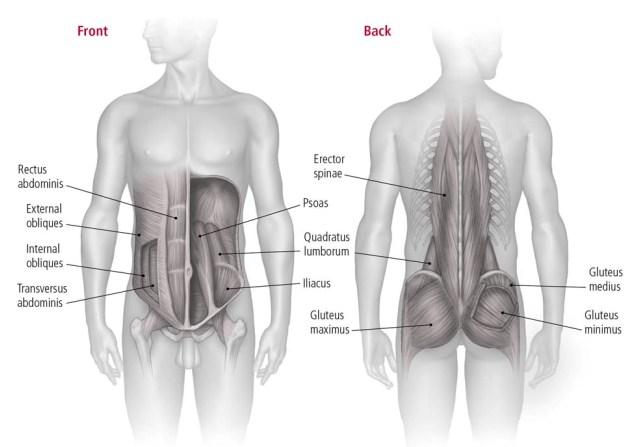
- Early - Responsible for flexibility of stems and enabled in common during sitting.
- Tactical Turning - Deep stability that helps keep pressure within the abdomen during courageous exercises such as baggage.
- Obliques inside and outside - Help the rotation, side flexion, and resistance.
- Erower line - spine stability in extension.
- Multifidus floor, enthusiastic area, and the diaphragm - Frequently overlooked, these muscles are necessary for the mailing control and stability of the spine.
Effective main training program should be Both movements and stable Functions across the country in advance, posterior, and lateral chains of the fish.
What is the plank?
A Panel Is the isometric exercise you hold the opposite attraction, sown while supporting your weight and your feet. Your spine in a Neutral positionAnd the muscles on the front of your participation without a joint movement.
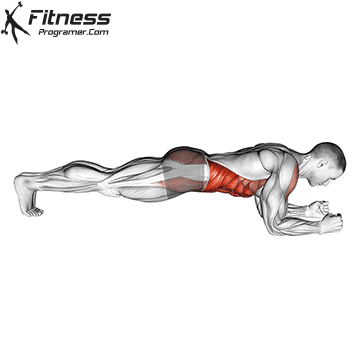
Key Benefits of Panel:
- Promote The stability of the spine And reduce too much lumbar movement.
- Train Tactical Turning And deep core muscles, which is hard to target the target with dynamic exercises.
- Able to converted with changes (eg, the side panel, RKC panel, high map panel).
- High offer Main Lake Value There is a low spine compression.
Planks were widely used in restoration, sports training, and general exercises settings for low risk of injuries.
What is the sitting?
Have Sit up The classical exercises that the candidate starts from a high position and lift the steering wheel on the knees. It's the main goal Early And, at the smaller level, the Hip flexors Such as IilloSoas and the fararoe femoro.
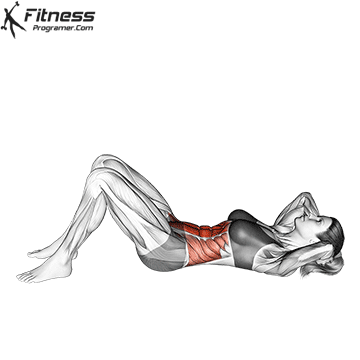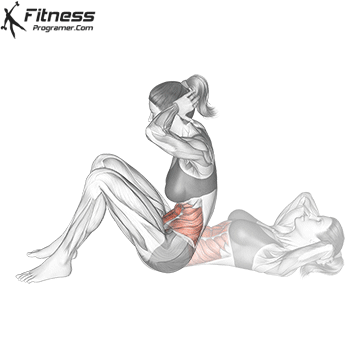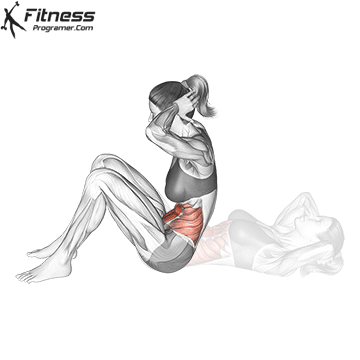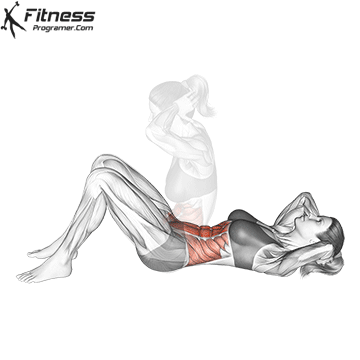
Benefits of sitting sitting:
- Construction Dynamic strength In the abdominal muscles.
- Promote An active spine stretchingWhich can improve the mobility at the time of control.
- Involved Hip flexors And other flexibility, contribute to all sports movements.
However, sitting on sitting is involved Repeated spine underloaded under loadWhich has highlighted concerns about the lumbar press pressure when performed incorrect or too much.
Comparison of muscle activation
| Exercise | Primary muscles have worked | Type of shrinking |
|---|---|---|
| Panel | Compensive abdominal, anus, oblique, multifidus | isometric (hold static) |
| Sit up | Rectus apoominis, hip flexors, obliques | Dynamic (focus / eccentric) |
While both exercises both stimulates, the Panel Excellent in development Postic Postic Strength And deep recruitment, while Sit up Very focused The strength of the movement In Artdominis anus.
Health risks in the spine and injury
This is probably the most described aspect of the panel compared to Semp comparison.
- Planks keep Spine And generally considered SafeEspecially for a person with a rear pain or sheet of pain.
- Sitting up, especially when taken with a rhythm or foot parking, can increase Press the lumbar spine and is cutting. Retoxion Retoritive, especially with bad form, may raise the risk of a disk herniation in a sensitive (McGill, 2007).
According to the mcgill spine biomechanics, planks are often Develop Core Security without compromiseing the spineWhile the sitting of sitting may have contamination in certain population.
Key Patience of Key Strength: What's Your Goal?
- If your object is building ToleranceStability, and mailing control for sports or long-term activities, Panel and its change Is better.
- If your goal is to develop Strength and power Through the movement of dynamic stems, especially for sports such as wrestling, gymnastics, or mma, Supports and flexible exercises Can also play a role-Provides the integrity of the spine is maintained.
Good shape programs may include both, but Planks offer less fluency and risk In the general population.
Programming instructions
For beginners or people with back pain:
- Start with Front planProgressing until it is considered a loople of more patience.
- Include Sideboard And Bird dog For intended resistance and responsive in rear chain involvement.
For an athlete or an advanced transfer:
- Form Dynamic plan (For example, shirt, pottery, pottery, drags drags) for increased challenges.
- Use Changes to sitting in controlLike Swiss ball crunches Or Dead bugSparingly and have a strict model.
Example Weekly Plan:
| Day | Exercise | Kit × Duration / reps |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Front plank | 3 × 30-60 seconds |
| Wednesday | the side plank (each side) | 3 × 30 seconds |
| Friday | Dead bug or control seat | 3 × 10-12 slow, control replies |
Conclude: which creates strong core?
Both Planks and Sit-Ups Offer utility - but they serve different objects. For most people, especially those involving health in the spine, mailing, or functional movement, Planks are a better choice. They make stability of a deep condom, minimize injury risks, and support sports performance throughout sports and activities.
Sitting of sitting can also be useful for aiming dynamic goals, but they should approach, without anxiety. In the end, the best Main Training Program Broken ISometric and dynamic elementsTo conjunction with mobility to create a durable and trunk trunk.
Ether
- McGill, SM (2007). Low back disorders: Prevention and restoration based on evidence. human kinetics.
- Ekstrom, RA, Donatelli, RA, RA, & Floor, KC, 2007). Electromynographic analysis of main stems, hips, and muscles at three muscle in recovery. J orthhop forts physically physically37 (12), 754-762.
- CT, CT, & McGGill, SM (1997). Low back load during many belly exercises: search for the safest belly challenges. Medications and science in sports and exercise29 (6), 804-811.
- Willardson, JM (2007). Stable training: Using sports sports programs. Journal of forces forces and research conditions21 (3), 979-985.
- Schoenfeld, BJ (2010). The mechanism of their hypertrophy muscle and their applications against resistance training. Journal of forces forces and research conditions24 (10), 2857-2872.
Source link