When we think about physical expression, we often imagine strength, speed, or patience. However, behind every seat, Sprint, or swing, is the deeper background: Inheritance skills. These skills are building a movement of movement. From the first step of the child's winning, learning skills that we move efficiently, adjustment, and excep.
In this article, we will search the basis of motor skills, differences between Hello versus the motor collectsThe steps develop motor, and why they are not only for athletes only, but for everyone from adult children.
What is the motor skills?
The motor skills are learning the movement related to the coordination of the brain, nervous, and muscular to produce a purposeful action. They are not purely true; They are developed through Repetition, action, and neurolic adaptation.
Example:
- A child learns to catch the ball is developing Visual coordination (Motor skills).
- Improved weightlighter improvements are updated Including motor-control.
- Master pianist learns sensitive fingerprintation of sensitive fingerprints High precision.
Mix motor skills Wisdom process (actions planning) And Physical practices (muscle activation). This is the reason they form the basis of all movement - from the basic daily activities such as walking and eating, complicated.
Hello versus the motor collects
Middle differences in motor skills are Hello versus the motor collects.
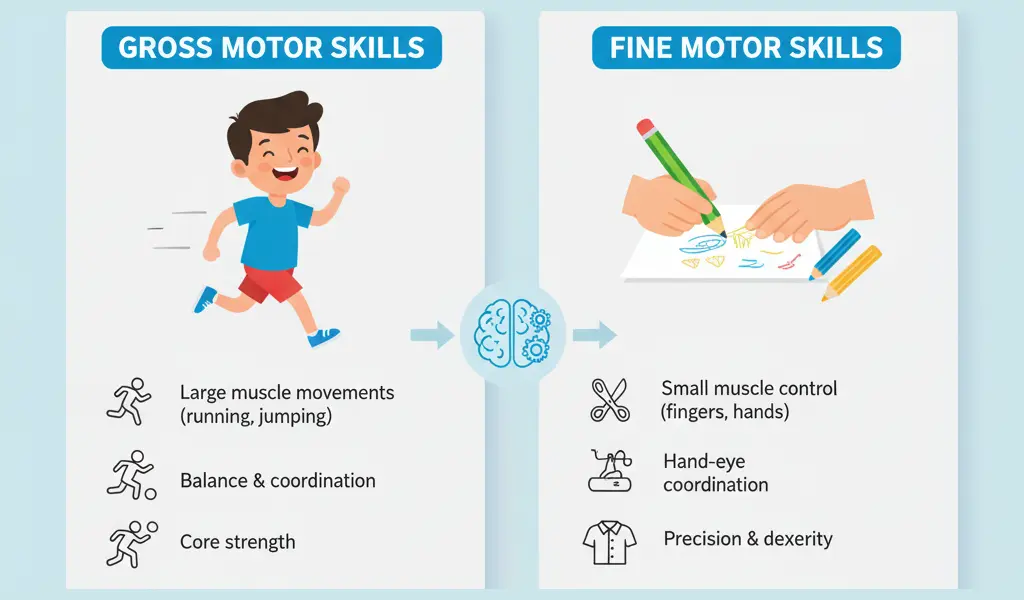
Including motor skills
The gross motor skills are large muscle groups and all body movements. These skills are required for ClapStrength, coordination and active.
Examples include:
- Walking, running, and jumping
- Throw the ball
- Performance squats or push
- Stroke float
The gross motors in the gross motor is important for an athletic and unique action. Without the coordination of a well developed motor coordination, even a simple job such as the climbing stairs or maintains.
Good skills
The good motor skills are related to smaller muscle groups - especially in hand, finger, and wrists. These skills require Precision, skilled, and control.
Examples include:
- Writing or drawing
- The shirt
- Printing on keyboard
- Control Strength strength In sports (eg, tennis, climbing
Good motor skills may seem less important for athletes, but it is important Sports required precision-Terestrics, gymnastics, martial arts, and even lifting weights where the necessary control and control necessary.
Motor Development Stage
Motor skills develop across a Throughout lifeStart in childhood and continue through growns. Understanding these stages, coaching, and parents support growth and appropriate performance.
1. Reflection move (0-1 years)
- Responding to unfind for Stimuli (GRAP Resexx, reflection.
- The basis for voluntary movements.
2. Antimental movement (0-2 years)
- Basic volunteering control happens.
- Roll, crawl, sit, walk.
3. Basic movement period (2-7 years)
- Basic skills developing: running, jumping, throw, catch, catch.
- Children learn movement modes through play.
4. Advanced movement period (7-14 years)
- The skill becomes refined and modified for sports or activities.
- Transition from "play" in structured training.
5. Live programs (14 years)
- Recognition through action and sports specific training.
- Adults adjust the motor skills to be a personal target (athlete, fitness, or daily function).
- Later in life, the maintenance of the motor skill is important for independence and declaration.
Why a motor skills
Motor skills are not only for children or athletes - they are essentials across human life. Here's why:
1. Sports practice
- Coordination and efficiency: A athlete with a better motor skills to use less energy for motion.
- Reaction time: Requirement of the exercise to determine success in competitive environments.
- Purchase of Acts: From dribbling basketball to perform the olympics, all sports skills come from learning.
2. Daily functions
- Simple shoes - bundle shoe, driving, carrying up the machine based on motor skills.
- Improve a strong skill Independence and confidence In everyday life.
3. Preventing Injury
- Poor motor control often cause movement reimbursement.
- Ideal coordination and security will reduce the risk of excessive injuries and falls.
4. Brain health
- The motor skills and wisdom process is firmly linked.
- Research shows that Learning new motor skills helps to save brainImprove memory and troubleshooting.
5. Aging and Live Age
- Training the motor skill, mobility, coordination, and balance in aging.
- Defend the deal, one of the leading causes of injuries in old population.
How to Learn Motor: Science of Motorcycle
The purchase of motor skills related to both Brain And Body.
Main elements:
- neuroplasticity: Brain adjusted by creating strong neural paths to performance.
- FeedbackExternal feedback (from trainers or technology) accelerate learning.
- Learning stage: Wisdom (understanding work), Associate (new update), independent (automatic action).
- Repetition with changes: Dark skills that are under different circumstances enhance adjustments.
Athletes and teachers use The learning principles The training of training sessments that improve coordination, efficiency, and adjustment.
Exercise to improve motor skills
The motor skills can always be developed - you are children, adults, athletes, or adults.
Motor Motor Complete Compos
- Prompt Stairs (coordination, coordination)
- Pierce drill (reaction time, speed)
- A balanced board training (stability, assistance)
- Weighing strength free weight (all body coordination)
Exercise on a good motor motor
- Grip's love (hand coordination, skilled)
- Balls that are thrown to the piercing with small objects
- Skilled exercises (piano, printing, or putty treatment)
- Clear sports performance (archery, darts, table tennis)
For an older adult
- Tai Chi (equilibrium, controlled movement)
- Walking with different areas (coordination)
- Light resistance training (motor recruitment)
- Useful function (carry-up, curved)
Motor skills in sports
Athletes often sepirate them by the expertise of motor skills:
- Basketball Competition: Dribbling requires a good motor control of the finger and coordination of gross motor for agility.
- Cup: To arrange the ball, balance, and agility dependent on the skills that are clear.
- Gymnastics: Include good control (equilibrium, balance) with gross motor forms.
- Weight: Comprehensive coordination and comprehensive coordination of multiple joints are necessary.
Even in the same sport, the athlete with a better control motor, the better often gets better fast and steady under pressure.
Improve the skill in training through training
For coaches, coach, or individuals, this is the instructions on evidence:
- Remarking importance techniques in load - Strength without coordination leads to poor motor development.
- Include clarity - Practice skills in different conditions (for example, dribbling in different surfaces).
- Use loobback loops - Video analysis, coaching solution, or wearing technology helps improve the movement.
- Gradually progress - Move from the basis to a complicated task.
- Combination of brain challenge - Training work twice (Movement + mental tasks improve the brain and motor duties.
Summary
The motor skills are The basis of all movement-FROM daily activities provide elite sports displays. Understand the difference between Hello versus the motor collectsRecognition of development, development and training them can help add effect, improve health, and promote independence.
Whether you are the athlete who seek the highest performance, parents support child development, or balanced adults, your journey. By investing in active skill and physical coordination, you not only train your body, your well-being, and your welfare.
Ether
- Gallahue, DL, Ozmun, JC, & Goodway, JD (2012). Understand the development of bike development: children, children, adult, adult (7 ed.
- Payne, VG, & ISAACCS, LD (2017). Develop human motor: How Lifespan (9 ed.). routledge.
- Schmidt, RA, & Lee, TD (2019). Learning and Action: From the Correction of Application (Dating 6). human kinetics.
- Haywood, KM, & GETTEL, N. (2020). Development of life motor span (7 ed.). human kinetics.
- Clark, Je, & Metcalfe, JS (2002). The mountain of motor development: comparison. In Je Graw & JH humhrey (EDS.), Research and review (PP. 163-190). NASPE prints.
- Adolph, Ke, & Robinson, SR (2015). The path to walk: what learns to walk us about developing. In A. Slayer & PC Quinn (EDS.), The developmental psychology: Classic Education (PP. 102-120). Sage Publications.
- Barnett, LM, et al. (2009). Teenage skills skills as a prediction of adolescence physical activity. Scientific and medical journal in sports, 19 (3), 267-272.
- Williams, HG, PFEIF, KA, JR, ML, Brow, RR (2008). Practice the motor skill and exercise in kindergarten children. Obesque, 16 (6), 1421-1426.
- Voelcker-Rehage, C., & Naemann, C. (C.
- World Health Organization (2019. Exercise instructions, sedentary behavior and sleeping for children under 5 years. Geneva: Who is.
Source link