Pre-nutrition There is an important role in determining how effectively you practice, how do you feel when exercises, and how will you get to the exercise. Many people believe that eating the snacks of sugar or drinking energy drinks before the training is the smart way of boost. After all, the sugar is a quick sub-digestive digestive that supply white sugar, body fuel.
However, sugar can build a short-term power of energy, consuming it too much before the training will often make training. Instead of being sustainable and forceful forces, you may experience powerful accident, mental rush, and even the discomfort of your exercise. To be the best for action, it is important to understand that sugar affects the body, why the default, and the exercise strategy before workout.
Science of sugar and energy burning
1. How to cook sugar in the body
When you consume food or drinks with flesh, bread, bread, bread, or sweet drinks, buds. This glucose into the bloodstream, causing blood sugar level. In response, the insulin puts insulin, hormones are responsible for transporting sugar into energy or immediate storage.

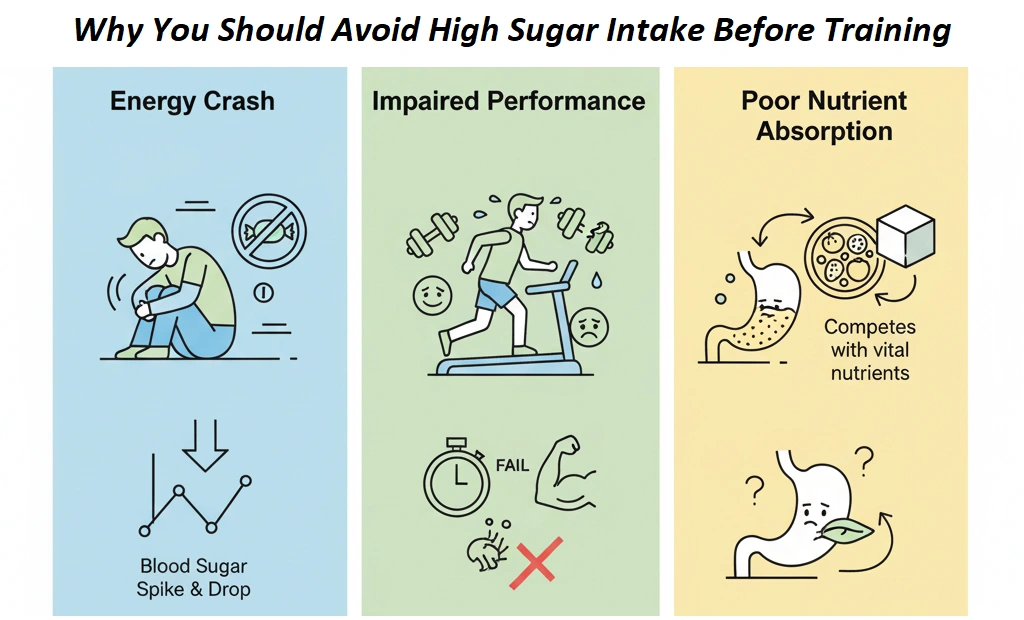
- Spiked phase: Initial increase in blood sugar, the blood sugar is temporarily boost.
- Accident phase: Overshoot insulin may cause blood sugar drop the bottom, making you feel shaped, or nonsense.
This cycle is known as Hypoglycemia reactions And as a general consequence of sugar consumption with large quantities before the training.
2. The role of glycogen in exercise
Muscles in glucogen mode in the form of glycogen, which is the main source of energy during exercise. While taking some sugar can help glycogen fill the glycogen, consuming it before the training should not need to improve the performance. Instead, the complicated complicated carbohydrates provide a steady sugar release and support lasting power output.
3. The hormone effect
In addition to the blood sugar, the high sugar obtains influences the most hormone:
- Insulin: Spike rapidly, followed by drop, which may affect fat burning during exercise.
- Cortisol: The stress hormone may increase if blood sugar, add weakness and perceived.
- Dopamine: Sugar stimulates prize roads, but depending on reducing natural incentives and creates dependence.
Why get high brown before the train can have problems
1. Middle accidents
The largest problem with high brown sugar is Energy accident That follows the cartridge initially. Instead of a steady power, you may feel suddenly tired of your conference. This is a particular danger during strength training or impatient exercises that require a consistent effort.
2. Reduce fat use
When the blood sugar level and insulin has been upgraded, your body explains Glioritizes burned more than suction of fat stores. For athletes or individuals aimed at improving the body composition, this can restrict the efficiency of fat loss.
.. difficulty concerned
Dietary drinks and snacks can cause abdominal pain, or nausea during eating, especially during the patience or patience. Fluids with high-brown concentrations (as a soy of soy or fruit juices) can also delay the stomach, causing discomfort.
4. Mental Rush
The sugar accident is not only affecting physical power - it also affects the brain work. Reduced blood sugar can lead to bad focus, slower focus, and low-motivation during exercise.
When sugar may be useful in training
Not all sugar is harmful in physical condition. In fact, there is a strategy when consumed simple carbbs can be useful:
- During the endurance exercises (90+ minutes): Sports drinks, gels, or fruit can give sugar to maintain glycogen levels and often fatigue.
- Post-workout recovery: Moderate simple carbs combination with protein helps replenish glycogen and accelerate muscle repairs.
- High Violence Competition: Athlete who needs a fast energy system (for example, sprinters, crossfit competitors may benefit from fasting carbs before events.
The key returning that sugar can be a tool - but only time the right time and consumed in moderation.
Nutritional options before Works
1. A complicated carbon for steady energy
Instead of refined brown, select Complex carbs Subrier slower and let the sugar gradually. Examples include:
- Oatmeal with fruit
- Sugar rice or quinoa
- Sweet potato
- Bread across the seeds
These foods provide stable energy supply without spikes or accidents.
2. Includes no protein
Adding proteins to diet before exercises helps keep the fullness, sugar stability, and muscular repair. Example:
- Chicken or turkey to enter
- Greek yogurt with berries
- Protein based on plants
3. Healthy fat in moderation
Fat takes longer than to digest and inappropriately before the training, but a small amount can help sustainable energy when longer learning. Example:
- Butter Nut It has all the toast
- Avocado fruits
- Chia seeds or flax in smoothie
4. Absorice the water before
Water or electrical drinks are necessary for water balance, temperature, and patience. Lack of water, even 2% equals 2%, can reduce the practice.
Food Ideas Identity Before workout
1-2 hours before the training:
- Oats ends with bananas and almond butter
- Grilled chicken with potatoes and sweet vegetables
- Wrap all grain with Turkish, spinach, and hummus
30-45 minutes before the training (fast fuel):
- Banana with peanut butter
- Bread with Almond and Honey Butter
- Smoothie small protein has berries and oats
Special considerations by type of training
1. Strength training
Balanced foods with protein carbs and complex 1-2 hours performs Glycogen store and protection. Avoid the sugar with the brown fluctuations in the middle of the meeting.
2. Patience training
For running or bike under 90 minutes, complicated carbbs and suction is enough. For longer events, simple carbbs in exercise may be helpful.
3. Hiit distance training (hiit)
Stable energy from complex carbs prevent from the early extent. The high sugar reception hiit Can lead to accidental captivation and reduce yield.
4. Exercise and weight loss General
Those training for Weight Or the body's ingredient should avoid high sugar reception, as it reduces fatal sugar and may stimulate the trigger.
Long-term strategy to reduce dependence on sugar
- Plan food first: There is a balanced diet preventing the choice of snacks that are mean at the last time.
- Improve Sleep: Enough relax reduction for fast digestion.
- Manage stress: Meditation, deep breathing, and Cortisol-Driven Corevings Cortisol-Driver.
- Retras Budget: Gradually reduce the sugar addition to help the body adjust and make the desires in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it bad to eat fruit before exercise?
No. All the fruits like bananas or wild berries but also gave fiber, and minerals and minerals. They have a better option than a cooked food.
2. Should I avoid sugar before the training?
Not always. The amount of natural sugar from the fruit can be useful, but there are many quantities from processed foods should be avoided.
3. What if I have time just a fast snack before exercise?
Select a simple but balanced option like a banana with butter, low-brown bar.
4. Energy Drinks are effective?
Many energy drinks are high in sugar and caffeine. While Cafe Cain may be able to increase efficiency, sugar content can cause accidents. Sugar notion is often better.
Summary
While sugar can send fast energy, more volume consumption before the training is often obstructive than helping it. Blood sugar accident can reduce patience, strength, and focus on the conference, while still contributing to fat.
A smarter strategy is to use your body with a balanced diet, which is well-behaved food, and healthy fat and support. For most of the exercise, this method can cause food or drinks with the older tissue. The only exception is a long-term effective event or physical restoration, which uses simple carbs can play well.
By choosing options with additional information, you will not only avoid mid-construction, general, general results, and general results.
Ether
- Gameeendrup, AE (2014). Getting the carbon during exercise and action. Nutrition.
- Ludwig, DS (2002). The glycemic index: the university mechanics involving obese, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Jama.
- Ivy, JL (2004). Regulations of muscle glycogen replacement, muscle protein synthesis and repair of exercise. Journal of Science and Medical.
- Benton, D., & Young, ha (2017). The role of sugar in the intelligence functions. Food Court.
- Burke, LM et al. (2011). Carbon for training and competition. Sports scientific journal.
Source link