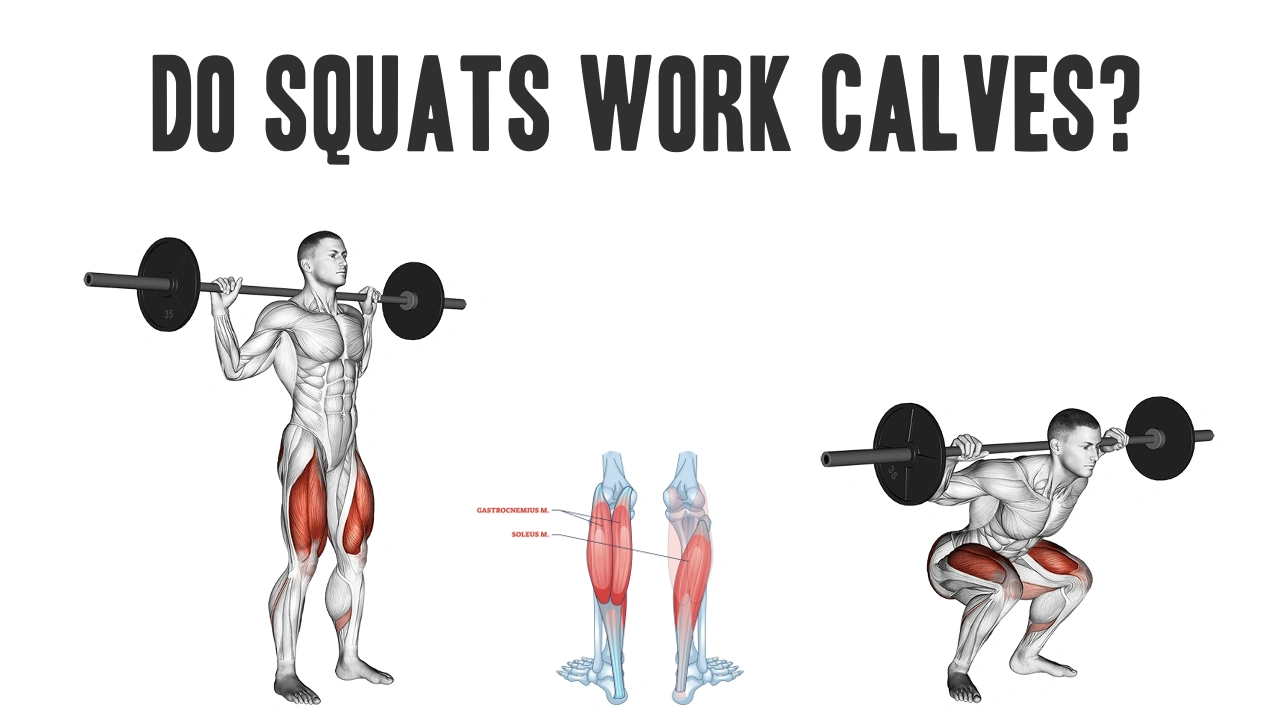
Squat was hailed as a king of the lower body exercises - target - similar key muscles Quads, Walking stickAnd glutes. But what about calves? Many people watch over the role of Calf muscles During the squat. Does the bag actually train them?
In this article, we will check the enemies during the seating, which muscles are active, and how to have a calm's exercise.
Calf Muscles: Brief overview
Have Complex calf Consisting of two main muscle:
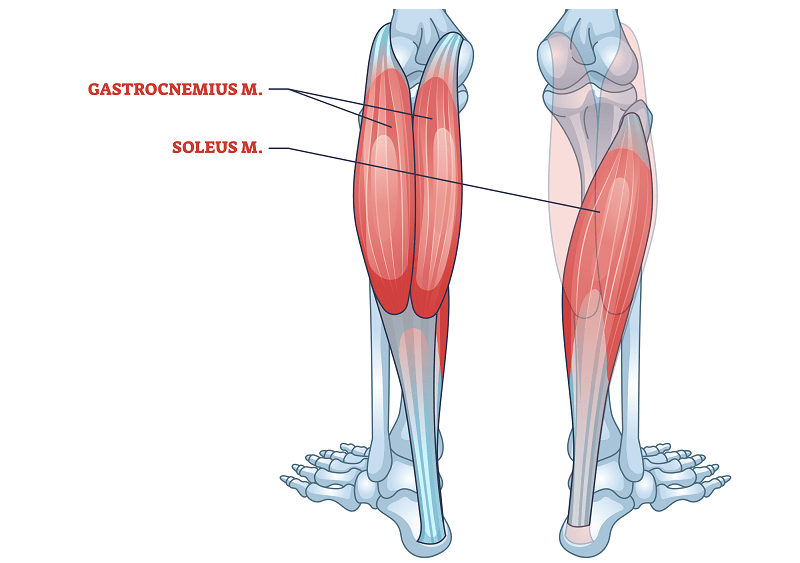
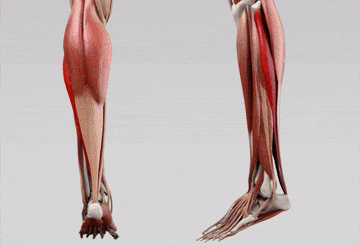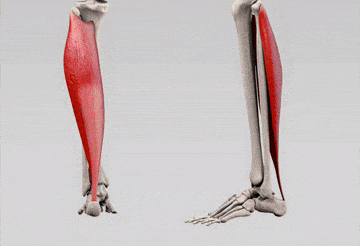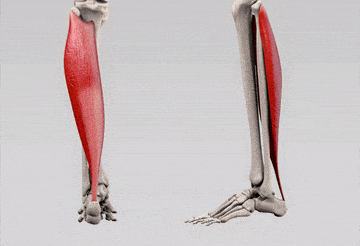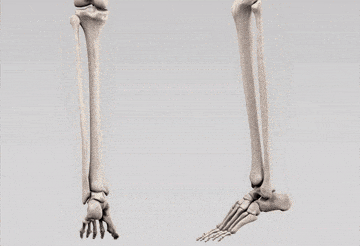
- gastrocnemius - The muscle of a large calf, noticed the knee and ankle.
- Top of a building - Deep muscle at the bottom of the Gastrocnemius that crosses just ankle together.
Together, control these muscles Spread (Pointing down to foot down) and be stabilized against ankle during movement and dynamic movements.
Squats do the calves?
Brief answer: Yes, but Indirectly and isometrically.
Here's why:
During Squat:
- Have Join together Remain relatively (especially in standard based seats).
- Have Top of a building Yes isometrically active To stabilize the ankle and help you maintain balance.
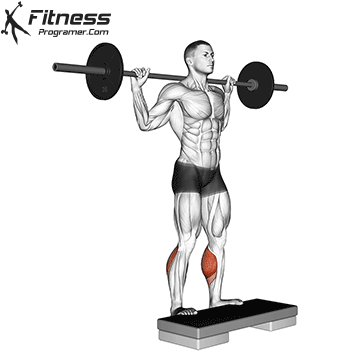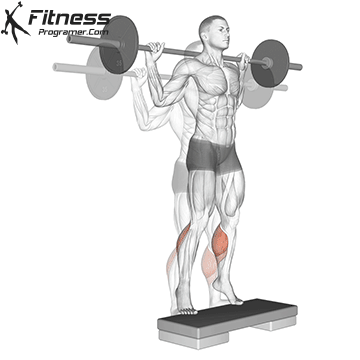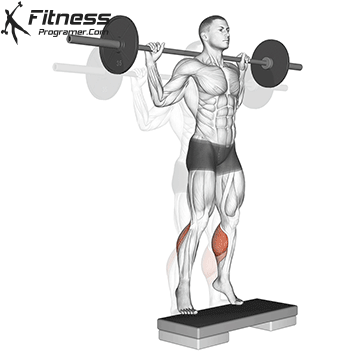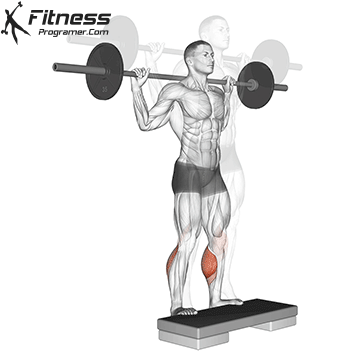
- Have gastrocnemiusWhich crosses both ankle and knees, there is Restricted stimulus Because the knee is bent throughout the movement.
Support evidence:
EMG studies suggest that calf muscles are Enable low level to moderate During the squats -minly to stabilize the body during the descence and the ordent period, not to ride the movement.
Important studyCaterisano et al. (2002) Show that while quads, glutes, and hamstrings show high promptings, displayed baskets Lowness engagementWorks as main as StabilityNot a driver.
Working the muscles of the calf during Squat: Phase by the distance
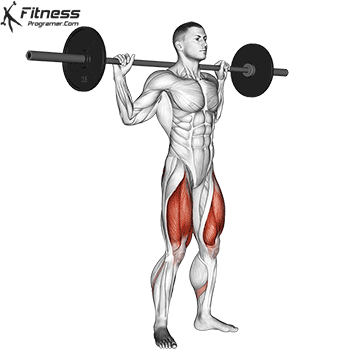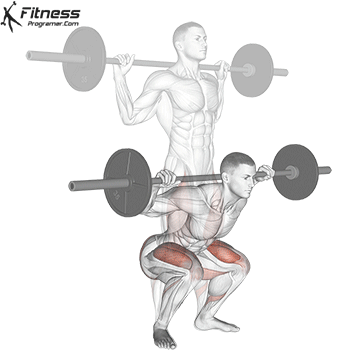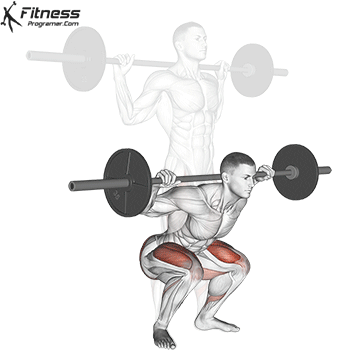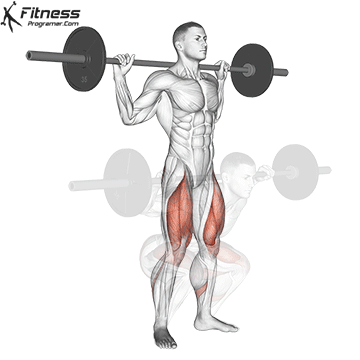
1. Descent (eccentric term):
- Body decreases by stretching hips, knees, and ankles.
- Have Soleus isometrically contract To maintain ankle stability and prevent the collapse at Dorsiflexion.
- Have gastrocnemius Mainly active due to the reduced knee of the knee.
2. Bottom position:
- The maximum of dorsiflexion's ankle.
- Have Safely safety To stability of tibia.
- If weighted weight (high heel), ankle restrictions, ankle restrictions will be reduced, changing the calf involvement.
3. Ascent (concentration period):
- hips and thighs to stand up.
- Safely safetyAgainst backward ankle backward.
- Minimal contribution from the gastness unless performance of data on the ankle on top.
How to increase the calf involvement in squats
If you are looking to form the muscles of a lot of cows during physical training, consider the following methods:
1. Perform squats to height of heel
- Importing the ends depending on the needs of the ankle data.
- This may make open a little soleus due to increased dorsiflexion levels.
2. Add a cow raising on top
- Mix squats with calf reades To integrated with a triientxion concentration.
- Common in useful exercises or training focused on hypertrophy.
3. Use pumines squats
- Delayed cessation and isometric increase stability requirements, promoting stressful calf stress.
4. Try to change the front container
- Goblet or front Squats change the center of your gravity, requires the stability of the ankle and the body.
Better choice aimed at the target of Cafves directly
While squats include calves on a small level, they are Not fit for calf hypertrophy or strength. To Target Calf Muscles:
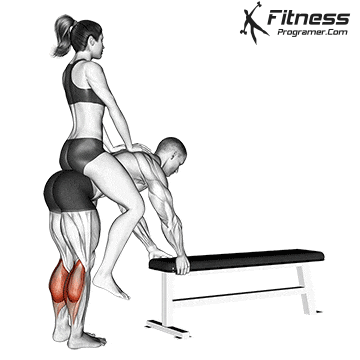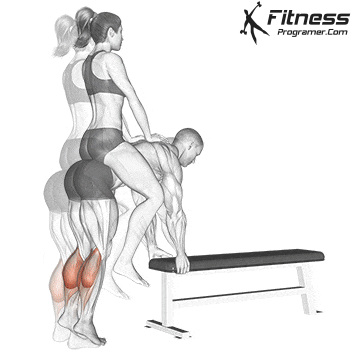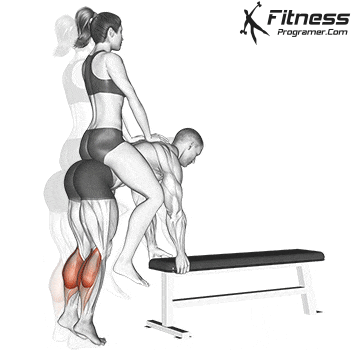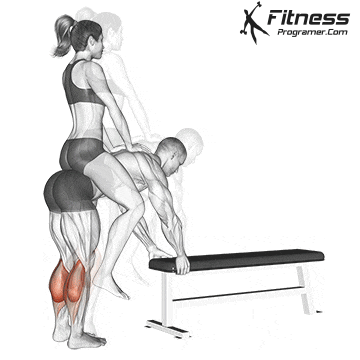
- Stand in constipation (Gastrocnemius goal)
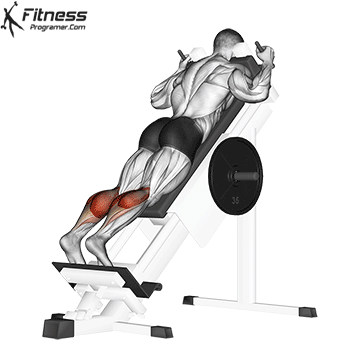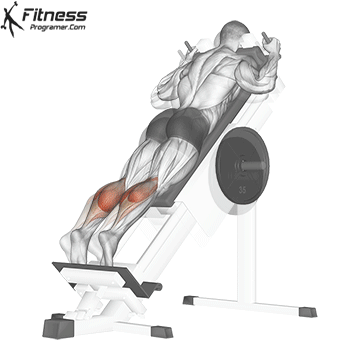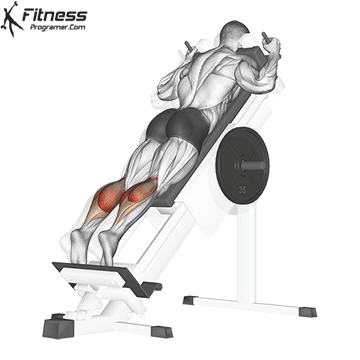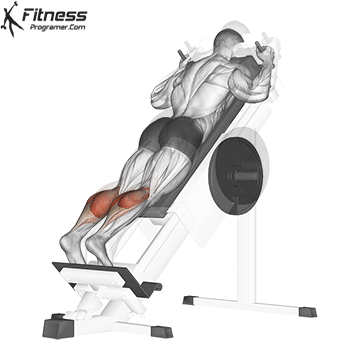
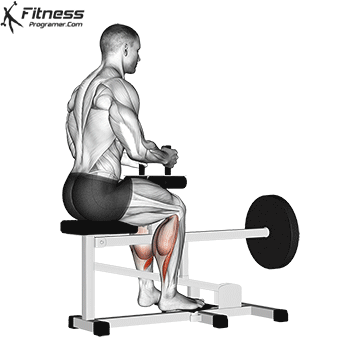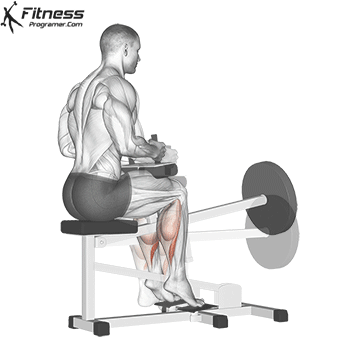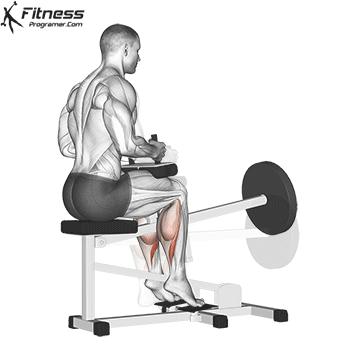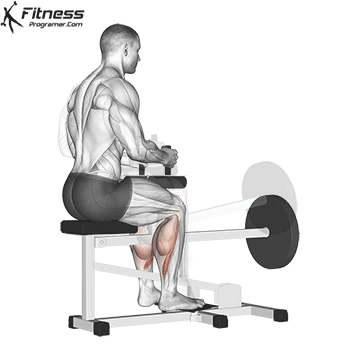
- seated calf uplifting (Emphasized soleus)
- Donkey Calf Pack (Emphasis for gastrocnemiumus)
- Cascase the electrical or plyometrics (For the engagement of bombs)
Conclusion: Are enough squats for calves?
Rarely. Squats do engaged with calf muscles, but primarily for StabilityNot an important pain. If you are serious to develop your crowd - whether it is beauty, practice, or injury prevention Calf Training Should be part of your project.
However, squats are important part of the physical body normal, and their indirect stimulus contribute to the ankle and knees together.
Ether
- Caterisano, A., moss, RF, W., W., W., W., W., W., W., W., W., W., W. The impact of Squat's depth return to EMG activity of 4 hips and leg muscles. Journal of forces forces and research conditions16 (3), 428-432.
- Escamilla, RF (2001). Biomamicics Knomenics the knee of dynamic squat exercises. Medications and science in sports and exercise33 (1), 127-141.
- Schoenfeld, BJ (2010). The mechanism of their hypertrophy muscle and their applications against resistance training. Journal of forces forces and research conditions24 (10), 2857-2872.
- Konrad, P., & Schmitz, K. (2008). EMG's front education of the ankle's ankle is straight over squats and other useful tasks. Magazine of ElectromyGaphy and Kinesiology18 (6), 907-917. Linked to an abstract
Source link