In sports and strength, high-level performance is never built in single physical quality. Instead, it is Relevant component relevant componentsExcited Strength, power, speed, agility, flexibilityAnd Tolerance-That creates a athletic edge.
As an emphasis in Bompa & Carrera Trade Model And supported by Study of Peer-Reviewed ScienceDon't do most of the ingredients often increase more efficiency. This article provides an overview of experts on how these ingredients are involved and how to train them effectively.
What is the exercise element related to the practice?
These are the necessary physical features for Specific Sport practice. Unlike health related ingredients (for example, body ingredients, cardiovascular health), Characteristic associated with performance There is a responsibility for:
- Explosive movement
- Sustainable output
- Explore Express Direction
- The ability to work long run
They must be trained together, not in loneliness.
1. Strength: the foundation of all physical quality
Definition: The ability to build resistance resistance to resistance (Force × Aurfe).
Why is it important: Strength is basic for development Power, SpeedAnd Injury prevention.
"Strength is a adjustment that leads to other adjustments you really care." - Charles Staley
Training Type:
- isometric (stability): Planks, Gymnastast
- Dynamic: Squats, Deadlifts, Click Bench
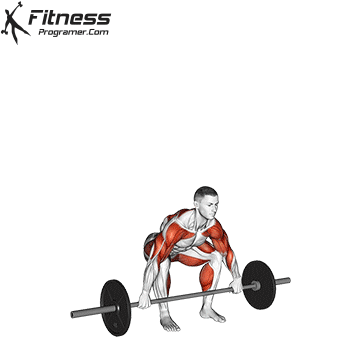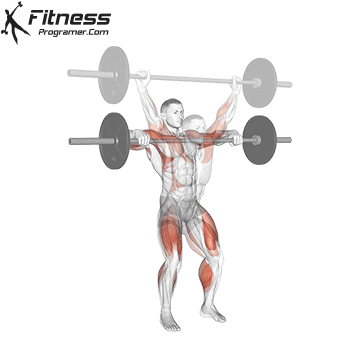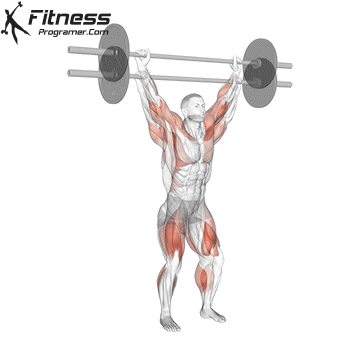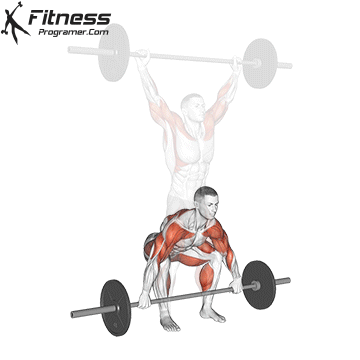
- Authorities: Treet Olympics
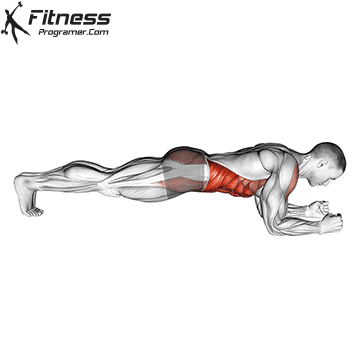
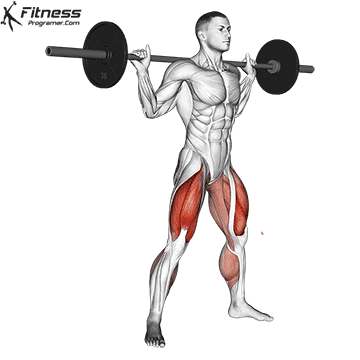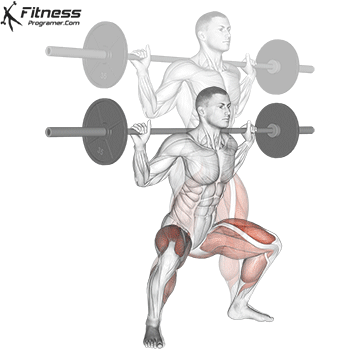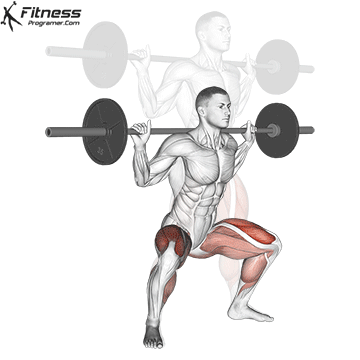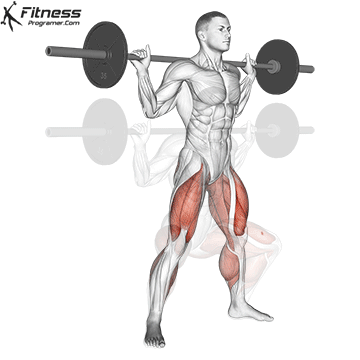
Proof: Strength training Reduce injury risk in young athletes (faigenbaum & Schram, 2004).
2. Power: Bridge between strength and speed
Definition: Power = Force × doom ÷ Time
Key characters: Mix Forces Lead The speed of the execution.
Application examples:
- Treet Olympics
- Sweep
- Jumping
- Discarding
Understanding Research: Rising power There is relevant to Mandatory development Than moving speed alone (Bompa, 2015).
3. Speed: Maximum speed: Maximum speed
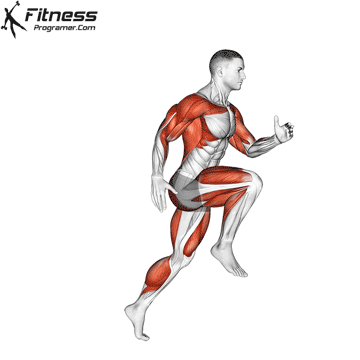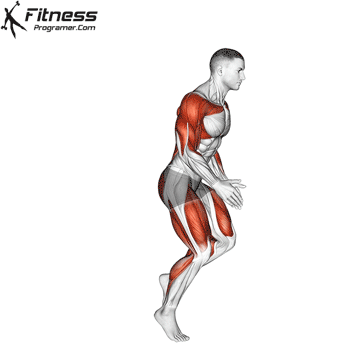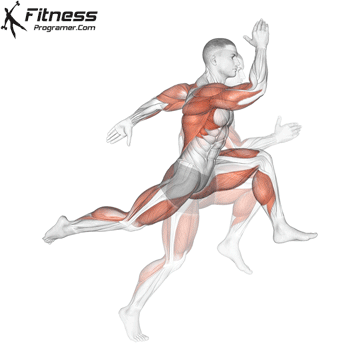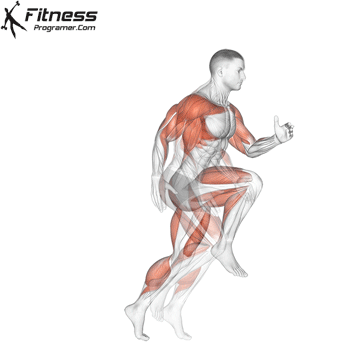
Definition: Speed = distance ÷ Time
Subhoor:
- Reaction time (respond to stimulus)
- Movement time (completed movement)
- Sprint speed (length of stride × moon the frequency
Training Revelation: Strong, effective muscles help add speed and maximum speed.
Note: Speed is Limited without strength And Update the coordination.
. Agility: Control changes in direction
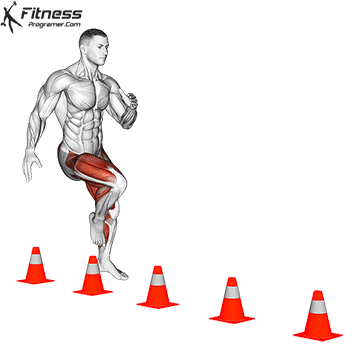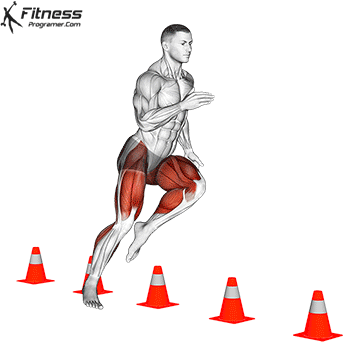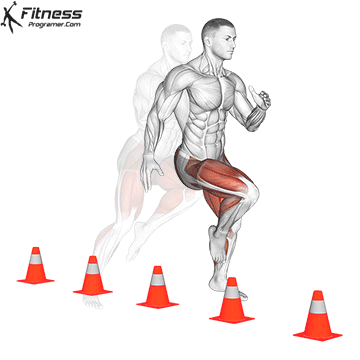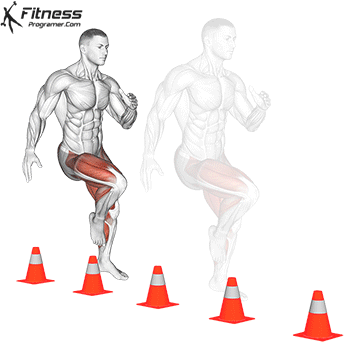
Definition: Ability to deception and change direction effectively.
Based on:
- Strength and power For the effectiveness of the effective / acceleration
- Controlling an anchor For the coordination and awareness of the body
Training Tips: Avoid the same drills throughout the year. Quick Training Must include Sports specifications To prevent the platelers.
5. Patience: Sustainable output during the period
Air patience
- Long, submaximal attempt (> 3 minutes)
- Example: Running distance, long suits
patient anaerobic
- Short degree, serious bombs (<60 seconds="seconds">
- Example: Sprocess, distance training
Muscle patience type:
| Type | Version |
|---|---|
| Continuous tension | Planks, climbing |
| isometric | Static Holds, ISometrics |
| Movement retotitive | Boat, high training |
| Short break / high attempt | Cycle Training, Football |
These types are available in Continue And often repeatedly dependent on sports requirements.
.. Flexity: Movemental Activity level
Dynamic flexibility:
- Perform before the training
- Enhance the joint movement without loss of energy
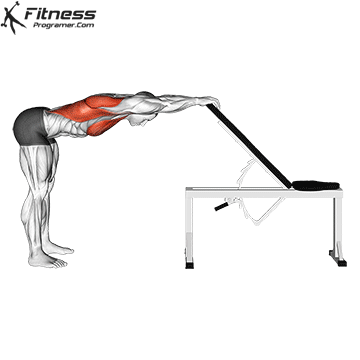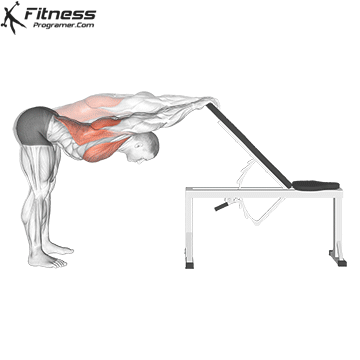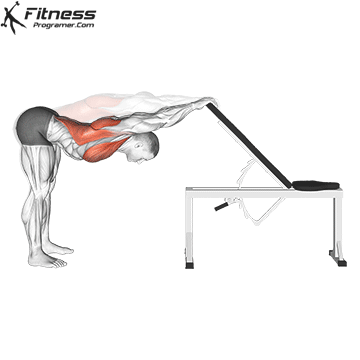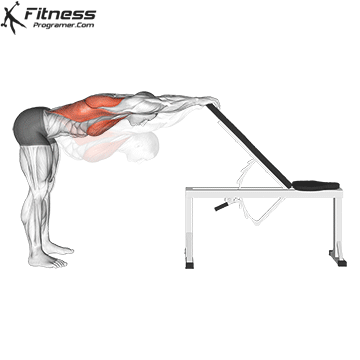
Fixed flexibility:
- Best after training
- Used for space with Tightly tightly (Based on check)



CUSAT Science:
Exercise before the essential Reduce strength and energy Up to an hour (Evertrovich et al., 2003; young and behm, 2003).
Specific uses:
- Exercher and Martial students call for high ROM
- Too much flexibility may block the operation in electrical sports (Jones, 2002)
7. Coordination and development of motor skills

Coordination include:
- Timepower
- Pace
- Spain awareness of the floor
- Original movement
What is the coordination Connect the raw physical energy. All athletes benefit from a successful training combination and supervision.
The training principle you must know
1. Specific: Training according to your sport or goal.
2. Excessive payment: Increases more intensity or quantity.
3. Change: Rotated to avoid the plateau.
4. Recovery: Remaining training effect - each of the qualities of each decomption at different rates.
| Adjustment | How long does it last (average) |
|---|---|
| Forces | 30+ days |
| Tolerance | 15-30 days |
| Speed | 5-10 days |
Conclusion: Why it works all together
Ingredients associated with performance does not operate in Silos. Your ability to jump, jump, change direction, or healing from fatigue is defined by means Well all your physical systems work together.
Whether you coach, athletes, or entertainment trains, construct the address Strength, Power, Speed, Patience, flexibility, and coordination In uniformity, advanced ways are the path to the display.
Ether
- Bompa T, Carrera M. (2015). Young air conditioner. human kinetics.
- Faigenbaum AD, Schram J. (2004). Can resistance training reduces injuries in young sports? Strength and conditions26 (3): 16-21.
- Evotovich Tk et al. (2003). Stretic effect stretching on the torque. J strength17 (3): 484-488.
- Young WB, Behm DG. (2003). The stretching and explosive displays. J Med Med Med Fitness43 (1): 21-27.
- Jones AM. (2002). Running vs Employment. Int J Med sports23 (1): 40-43.
Source link
