Push is one of the most accessible and effective and effective exercises. But you know that The speed you carry out the push you can influence a lot of resultsNot that you will be strong, size, or patience, Dimension Often, fast or slow or slow-speed encouragement can change your muscular approach.
In this article, we will search the science behind Very rapidly versusBenefits and shortcomings of each style, and how to choose the right pace based on your Target of exercise and training range.
Understanding in pushing
Dimension Refers to the speed you move through each period of exercise:
- Shake (Drop period)
- isometric (Pause at the bottom)
- Steal (Pushing phase)
Example:
- A Push fast May be done in 1 second decline, 1 second to up (1-0-1 minutes).
- A Push slowly May be 3 seconds down, vacation 2 seconds, and 3 seconds to (3-2-3 Temptount).
These data has a serious change Muscle Application, Power systemAnd Training updates.
Benefits of pushing fast
1. Energy strength and development
Fast push (eg, eg, applauding, pressure hops) IIF FREE-Type of fiberEssential for speed and yield to force the concentration. Benefits include:
- Useful for Energy athleteSports, fights and field sports
- Update The rate of development of forces (RFD)
- More than Explosion In sports (for example, sprinting, throw, jumping)
Many sports call The top force of the bomb body Production-g, DrillingPoint, dive, revenge. Quickly pushing the training Specific speed And Coordination mode Need in the real situation of the world.
2. Update neuroromuscular efficiency
Encourage pushing speed Communication of nervous system With muscle:
- Increase Recruitment speed
- Update Frequency and sync
- Develop Reactive strength-important for Quick And quick movements
3. Pardiovascular and metabolic synagology
Because of the faster and too fast repetition, push fast Heart rate Fast:
- Effectively in Hiit cycle Or Metabolic resistance training
- Update Cardioescatory patience
- Burns more Power per unit of timeEspecially when using over
Benefits of slow push
For coaches and athletes aimed at Rise to the maximumMerge Control, slow movement In their resistance training protocol is a highly effective strategy.
1. Great times under tension (Tut)
Slow pushing (eg, 3-6 seconds to rep) greatly Increase the muscles spent under mechanical loadThe hard drivers of hypertrophy. By slowing both eccentric (decreasing) and strength (push) (push), you create:
- More than Recruitment of muscle fibersEspecially Type I and III
- Update Metabolic pressure (Burn) that contributes to muscle growth
- Higher Intramuscular tensionWhich stimulates protein synthesis
Long contraction period Limit blood circulation (Oclusion)Causing the construction of lactate and other metabolites. This creates supportal hormone response:
- Muscle muscle (Eg: Growth Hormones Up)
- Update Local muscle patience
- "Pump Pump" that helps with muscle growth muscle
2. Improving Ming-Ming-Ming-Ming Connection
Slow pace helps Smuggling- The body's perception of the body to make it easy to feel muscles that are working.
- Enhance the correct form and stability, especially in beginners
- Branch Ideal alignment And joint control
3. Reduce tensions together
Because there MinorityConnect tissues (tendons, ligaments, co-Capsules) experience less shock. This makes a slow push:
- Safe for those who have Shoulder history of shoulder or wrist
- Ideal for Rehab or Prophab Project
- Better for Older adults or clients decide
Diligence of Diligent Training
1. LOW SIMIN LEAD LEAD DEADE LOADY FROM COMPLETRY AND Hytrophy
2016 Education Education in Journal of forces forces and research conditions Found Long eccentric term-as seen in boosting slow push push for push Great muscle activation and hypertrophy Compared to faster repetition. This shows the effectiveness of Control the movement and time under tension In the stimulation of muscle growth.
2. Tembos faster enhance neuroromuscular efficiency and energy efficiency
On the other hand, Tempy burst Has shown to the importance Improve Neurorcular efficiency and energy outputEspecially when integrated with Movement of weight or plyometric movement. Cormie et al. (2010) Show that high-speed training increases in receipt of Quick muscle fiberWhich is responsible for explosive movement, high explosive movement.
3. Slow fasting rehearses help adjust the strength and size in a trained person
Pereira et al. (2016), in their study "Resistance to the late speed of movement is better for strength of hypertrophy and muscle who is about to get more than the speed of movement," Found Slow repetition speed Cause increasing The cross area of the muscle and maximum strength of repetition In Trained adults. This challenge that the equation that advanced trains require only high loading or explosive explosives for advancement.
4. Patience and Volume: The fastest push
While pushing slowly increases, Fast pushing allows for all repetition Before fatigue. By 2020 Education Found:
- Participants complete 33% additional reps At a fast pace
- Anyway, slow push for allowing 20-24%%% than a whole time
Takeaway that practices
Slow hot symptoms allow More mechanical tensions, Recruitment of muscle fibersAnd Metabolic pressureWhich are known to stimulate muscle hypertrophy. Contrast, fast, explosions are different role in development Power and Sports PracticeShow that Styles with both forms with precious applications According to the training target.
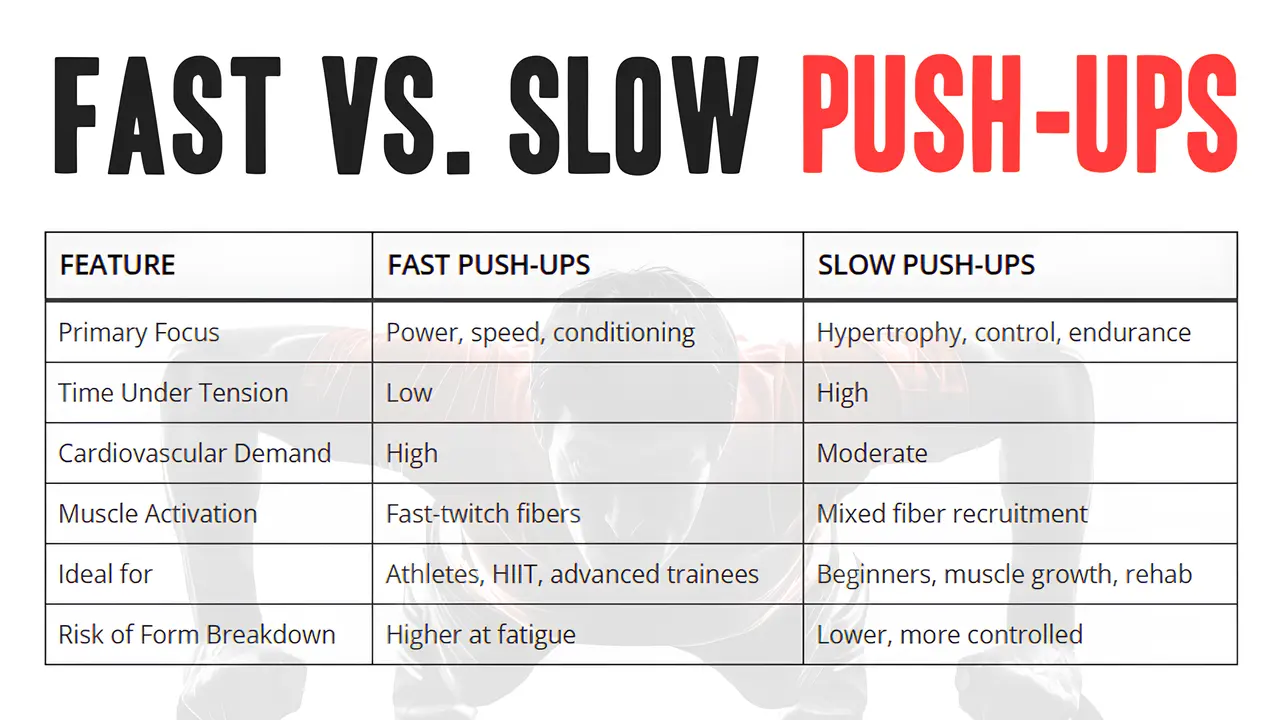
Fast versus Slow push: Side Comparison: Side Comparison
| Features | Push fast fast | Slow pushing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary point | Power, speed, air conditioner | Hypertrophy, Control, Patience |
| Time under pressure | Low | High |
| The needs of the heart | High | Fairly |
| The opening of a muscle | Fast twist fiber | Integrated replacement |
| Ideal for | Athletics, Hiit, advanced trains | Beginner, muscle growth, restored |
| The risk of division | Low | Lower, more control |
How to include both into your project
1. Use fast push for settings or electric packages
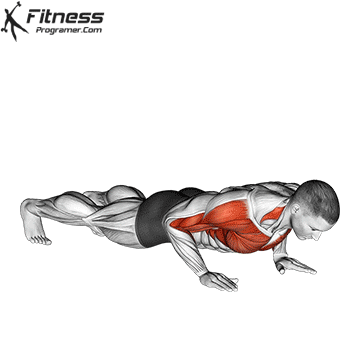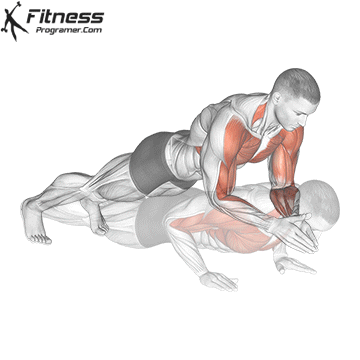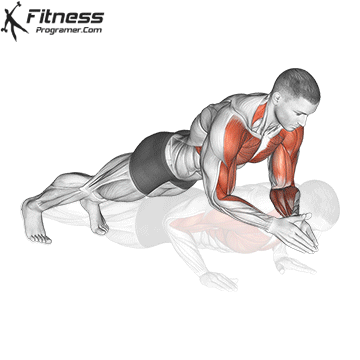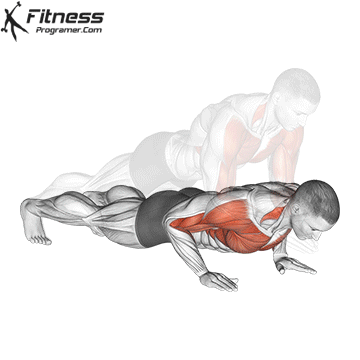
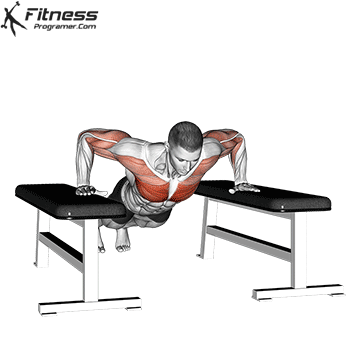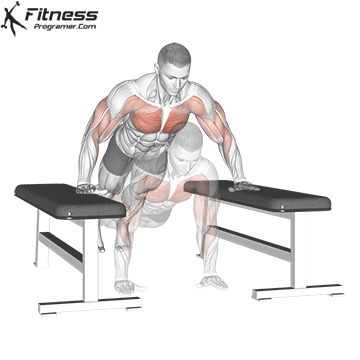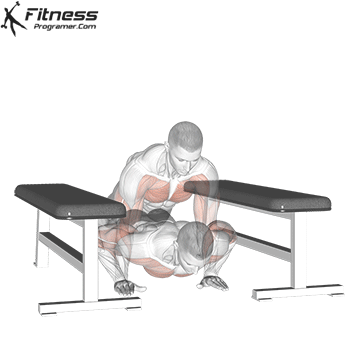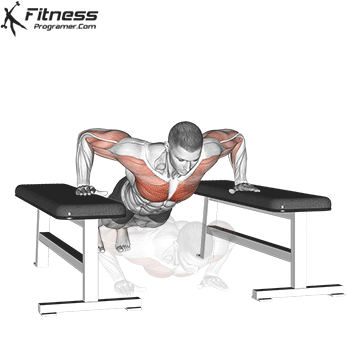
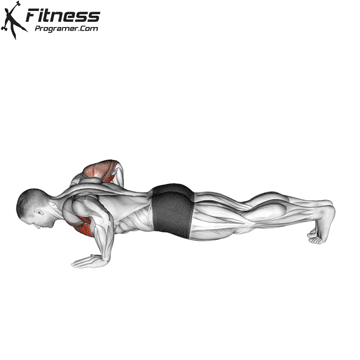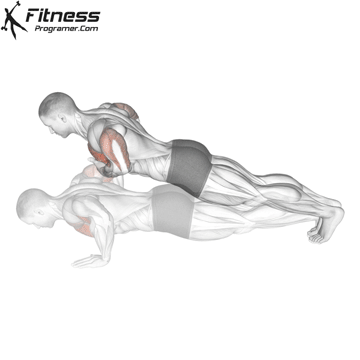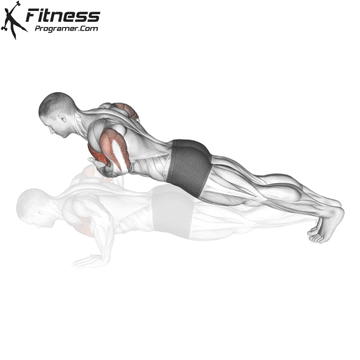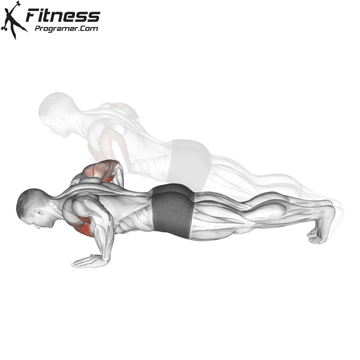
2. Use slow push for muscle construction and mechanical
- 3-4 seconds down, 1-2 second, 2 seconds
- Perform a 3-4 series to Failure For hypertrophy.
- Ideal for chest training and triceps-focapus
3. The opposite set of
- Superset with 3 sets of 10-12 quick pushing or plyometric push-ups
- 3 sets of 10-15 slow push-up (4 seconds eccentric + 2 SEC Certicic)
Changing Tembo Create A Complete training stimulus And defend the plateau.
Security Instructions
- Shoulders and arms Before pushing the bomb
- Preserve Neutral spine and scapular control
- Stop if decayed mode - especially high speed
- Don't sacrifice Range of movement For speed rep
Summary
The choice between fast pushing and slow not down to one that "better" - it's about choosing the right pace Current goal. Whether you find to rise Explosive strengthCreate MuscleJesus ToleranceOr simply maintained UnionBoth push and slow with their place in balanced exercises.
Understand how Influenced the training improvement Help you to train wise - not just harder.
Ether
- Pereira Yl, GJ Estter, LA, Tanaka Kh, Eyeveredo P. Anti-motion is better than the speed of movement. Int j appl exercise. 2016; 5 (2) Google Approla
- BUD, Na, Andrews, RJ, West, DWD et al. Muscle is under pressure during the resistance exercises help prompts the response to different muscle protein protein protein protein protein proteins in men. J Physics. 2012 https://pubmed.ncbi.ncibi.nih.nih.Gov/22106173/
- The opening of a muscle during changes with changes and various piercing. J strength. 2016; 30 (7): 2068-2073.
- Cormie P, Mcguigan Mr, Newton RU. Develop maximum neuromuscular energy: part of the biology of energy. MED sport. 2010; 40 (9): 717-740.
- Schoenefeld BJ. The mechanism of their hypertrophy muscle and their applications against resistance training. Joe res. 2010; 24 (10): 2857-27872.
- Medical and biological engineering magazine: The impact of the most trained speed to train until it's tireless (January 2011)
- American Sports University. ACSM advice for exercising test and prescriptions, 11 ed.
Source link